CBSE, CLASS 7,IT, COMPUTER, UNIT 2, FUNCTIONS AND CHARTS IN CALC
CBSE, CLASS 7,IT, COMPUTER, UNIT 2, FUNCTIONS AND CHARTS IN CALC
Notes
Mathematical Functions:
· ROUND() : This function rounds a number to the specified number of digits
Syntax: =ROUND(number; count)
Example : = Round(35.45;0) Answer : 35
= Round(39.95;0) Answer : 40
· LCM():This function finds the least common multiple of given numbers.
Syntax: =LCM(Integer1;Interger 2;.......)
Example : = LCM(10,5,15) Answer : 30
= LCM(2,6,8) Answer : 24
· GCD() : This function finds the greatest common divisor of given numbers.
Syntax: =GCD(Integer1;Interger 2;.......)
Example : = GCD(10,5,15) Answer : 5
= GCD(2,6,8) Answer : 2
Text Functions
· UPPER() : This function converts text to uppercase letters.
Syntax: =UPPER (text)
Example : = UPPER(“podar”) Answer : PODAR
= UPPER(“function”) Answer : FUNCTION
· LOWER(): This function converts text to lowercase letters.
Syntax: =LOWER(text)
Example : = LOWER(“PODAR”) Answer : podar
= LOWER(“FUNCTION”) Answer : function
· LEN() :This function finds the number of characters in text.
Syntax: =LEN(text)
Example : = len(“PODAR”) Answer : 5
Date & Time functions
· Date() This function displays the entered day, month and year in the mm/dd/yy date format.
Syntax: =DATE (year;month;day)
Example : = date(2022,10,6) Answer : 10-06-2022
· Time() This function converts the entered hours, minutes and seconds in 24-hour format
Syntax: =TIME(hour;minute;second)
Example : = time(16:25:30) Answer : 4:25:30 PM
· Today() This function displays the current date.
Syntax: =TODAY ( ) returns the current system date in the mm/dd/yyyy format.
Logical functions :
Logical functions are used to carry out comparison in your formulas or test multiple conditions. They return either True or False.
Syntax:=IF(logical_test,value_if_true, value_if_false)
Types of Error:
· #VALUE – the argument type given to the function is not correct
· #NAME? – misspelled function name or cell
· #DIV/0! – when a number is divided by 0
· # REF? – Deleting a cell or range which is used in a formula
· ##### – when the width of a cell is not enough to display the value inside it
Exercise
1. | Fill in the blanks. |
a. | The error means that there is an error in the formula, range or name of the function. |
Ans: | #Name? |
b. | The is a location-based cell reference. |
Ans: | relative cell reference |
c. | The chart is used to illustrate the changes in a value over a period of time. |
Ans: | line |
d. | The feature of the Calc worksheet allows you to rearrange data in an efficient manner |
Ans: | sort |
e. | The feature helps to quickly extract data from the spreadsheet that meets certain criteria. |
Ans: | filter |
2. | Identify the type of cell reference. |
a. | = C1 + D1 |
Ans: | relative reference |
b. | = $A$1 + $B$1 |
Ans: | absolute reference |
c. | = A2 + B2+ C2 |
Ans: | relative reference |
d. | = $B$1 + $C$1 |
Ans: | absolute reference |
3. | What will be the output of the following functions in Calc? |
a. | =UPPER(“Mango”) |
Ans: | MANGO |
b. | =LEN(“Social Studies”) |
Ans: | 14 |
c, | =ROUND(855456666; 3) |
Ans: | 855456666 |
d. | =TIME(22;30;25) |
Ans: | 10:30:25 PM |
e. | =GCD(80;6;8) |
Ans | 2 |
f. | =LCM(68;4) |
Ans | 68 |
3. | Answer the following questions. |
a. | What are the different errors that can occur while using functions in Calc? |
Ans: | · ####### - It occurs when data in the cell is longer than the width of the cell. |
· #Name? - It occurs when there is an error in the formula or range or name of a function. · #REF! - This is shown when a formula refers to a cell that is not valid. · #VALUE! error - This occurs when a formula has the wrong type of arguments. · #VALUE! error -It occurs when a formula tries to divide a number by 0 or an empty cell. | ||
b. | What is cell reference? Explain the different types of cell references. | |
Ans: | · A cell reference is the format used for addressing a particular cell in a formula or a function. · A relative cell reference is a location-based cell reference that calculates a cell’s location with respect to the location of the formula containing cell. · In absolute cell referencing, the cell reference used in a formula stays the same when you copy or move the formula to any other cell. · The mixed reference consists of an absolute column and a relative row (= $B1 + $C1) or an absolute row and a relative column (= B$1 + C$1). | |
c. | Why do we use charts in OpenOffice Calc? | |
Ans: | · Charts allow us to view data in a visual way. · This helps us analyse data quickly and effectively. | |
d. | Explain the following charts. Give an example of where they can be used. | |
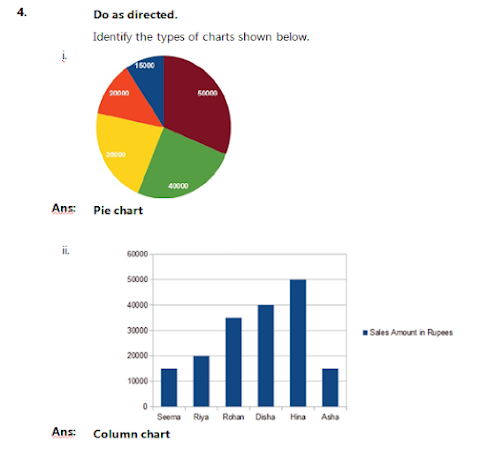
i. | Pie chart | |
Ans | It is used to show a breakdown of data in terms of proportion so as to display the contribution of each value to a total. | |
ii. | Line chart | |
Ans | It is used to illustrate changes in a value over a period of time. | |



Nice
ReplyDelete